What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The classification of a new body system, called the Endocannabinoid System, was discovered in the early 1990’s, paving the way for exciting new findings for treating certain diseases and promoting health and well-being.
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are the natural plant chemical compounds found in cannabis. There are over 100 different type of cannabinoids. The two most notable cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD).
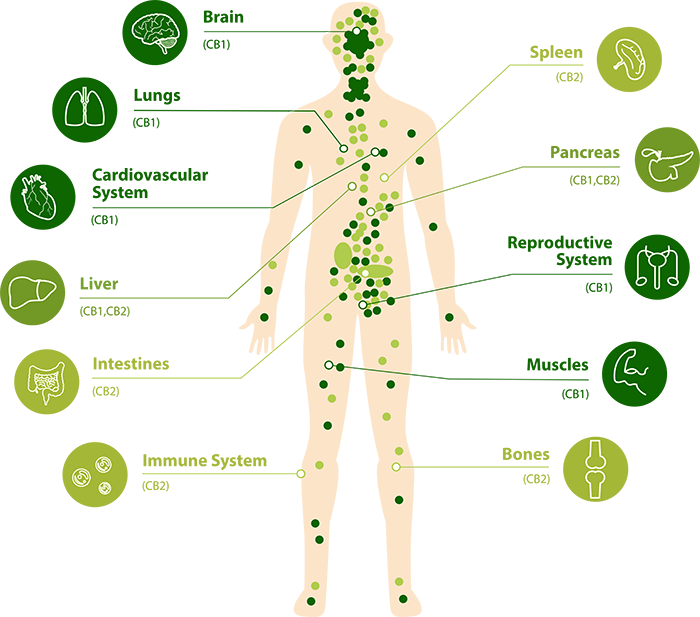
Endocannabinoids bind to Endocannabinoid Receptors in the body, to signal the Endocannabinoid System to function. The two main Receptors are CB1 and CB2.
CB1 is found in the central nervous system, helping to regulate nerve communication in the brain. CB2 is found mainly in the outer nervous system regulating the immune system and inflammatory pathways.

CB1
- Motor Activity
- Thinking
- Motor co-ordination
- Appetite
- Short-term memory
- Pain perception
- Immune cells
CB2
- Digestive Tract
- Kidneys
- Pancreas
- Adipose tissue
- Skeletal muscle
- Bone and Eye
- Tumours
- Reproductive System
- Immune System
- Respiratory System
- Skin
- Central Nervous System
- Cardiovascular System
- Liver
Endocannabinoid System
There are 11 main systems of the human body. Examples of which include the muscular, nervous, digestive, immune, endocrine, cardiovascular, skeletal and respiratory system. Twenty years ago, another body system was discovered called the Endocannabinoid System (the ‘ECS’). It is a biological, nerve signaling system, comprised of molecules called endocannabinoids. Scientists have only just begun to understand it, and are discovering more and more of its full potential functions.
Although the ECS remains under preliminary research, experts believe that it’s main role is to regulate the physiological, emotional and cognitive processes of the body (maintain homeostasis), such as sleep, pain, mood, reproduction and appetite.
The human body naturally produces endocannabinoids, to balance and control communication between cells.
Cannabinoids mimic the functions of endocannabinoids and can help to address any imbalance within the body.
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM:
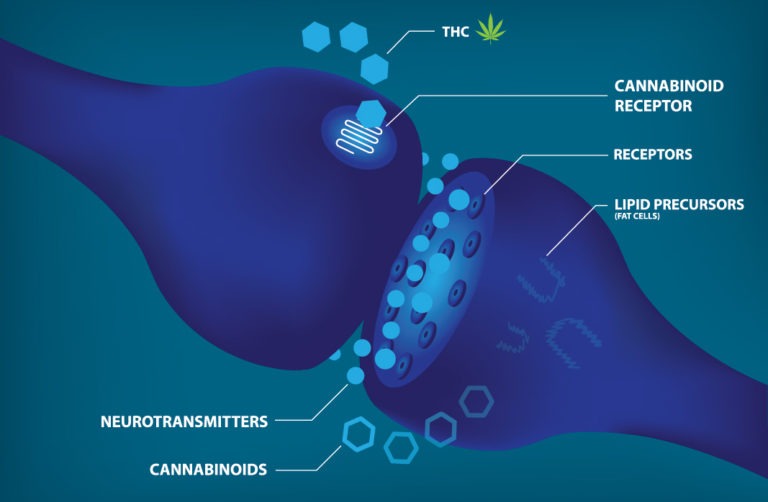
Brain Cells (neurons) communicate with each other by sending chemical messages. The chemicals (neurotransmitters) cross a gap between neighboring neurons before attaching to their specific receptors.
Presynaptic:
The neuron sending a message by releasing a chemical when signalled to do so
Postsynaptic:
The neuron receiving the message when its receptors are activated by specific chemicals (neurotransmitters).
Neurotransmitters:
The chemical messengers that travel from one brain cell to another.
Receptors:
Activated by neurotransmitters, receptors trigger a set of events that allows a message to be passed along to other neurons.
Cannabinoids:
Natural chemicals (anandamide and 2AG) that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and the body.
THC:
The main active ingredient in marijuana: THC interferes with the normal functioning of the endocannabinoid system.
What is CBD?
One of the main cannabinoids found in cannabis is Cannabidiol and is known as CBD. CBD in particular has been found to give a wide-range of positive health benefits through its interaction with the body’s own endocannabinoid system.
The other main cannabinoid found in cannabis is THC. However, unlike THC, CBD is totally non-psychoactive allowing for the utilization of CBD properties without getting you ‘high’. CBD is typically derived directly from hemp plants that are naturally high in CBD. Hemp is the cousin of the marijuana plant and is simply classified as cannabis with <0.3% THC.

How Does CBD Work in The Body?
Potential benefits of activating the CB1 Receptors
- Lower anxiety
- Lower blood pressure
- Lower intestinal inflammation
- Relieve depression
- Reduce fear and paranoia
Potential benefits of activating the CB2 Receptors
- Help with alcohol and nicotine addiction
- Increase appetite
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Reduce chronic pain
- Reduce inflammation
- Stress response
Researchers are aware of the advantages of CBD for the human body, and are looking into ways for CBD to help in the following areas:-
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Sleep disorder
- Anxiety and Stress
- Epilepsy
- Addiction
- Parkinson’s Disease
